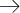According to GeoStat data, real GDP growth was 0.8% in January and 2.8% in February 2016. While these figures are by no means high, growth rates in the rest of the region are expected to be quite low this year. In this respect, in contrast to its neighbors, Georgia is performing reasonably well.
According to the World Bank GDP forecast made in January 2016, the Georgian economy will grow by 3.0% this year, which is above the expected growth of Eastern Europe (0.5%), Azerbaijan (0.8%), Armenia (2.2%), and Russia (-0.7%). The ISET-PI forecast for the first and second quarters of 2016 is 2.9% and 5.0% respectively. The recently updated forecast predicts 3.3% year-over-year real growth in 2016.
Total consumption of electricity increased by a mere 0.8% year over year in January. Electricity consumption through distribution companies increased by 4.3%, while direct consumers decreased their electricity consumption by 25.4% year over year in the reported month. According to GeoStat’s recent estimates, VAT payers’ turnover increased by 7.2% year over year in January 2016. Although VAT turnover is typically a good predictor of aggregate demand changes, data shows that the growth rate of VAT payers’ turnover may be a better proxy for nominal rather than real GDP growth in Georgia.